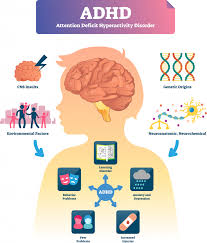
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Its core symptoms include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, which can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life. While there is no cure for ADHD, various treatments can effectively manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Among the most common approaches is the combination of medication and therapy, which offers a comprehensive approach to addressing the multifaceted nature of ADHD.
Understanding ADHD Treatment
Effective ADHD treatment aims to reduce symptoms, improve functioning, and enhance the individual’s ability to navigate daily life successfully. The approach to therapy is often tailored to each person’s unique needs, considering factors such as age, symptom severity, coexisting conditions, and individual preferences.
Medication for ADHD
Medication is frequently prescribed as a primary treatment for ADHD, particularly for managing core symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine-based drugs (Adderall), are among the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. These medications increase neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which play critical roles in attention and impulse control.
Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine (Strattera) and guanfacine (Intuniv), are also available for individuals who do not respond well to or cannot tolerate stimulants. These medications work through different mechanisms to help regulate attention and impulse control.
Benefits of Medication
Medication can provide significant benefits for individuals with ADHD, including:
-
Improved Attention and Focus: Stimulant medications can enhance attention and concentration, allowing individuals to better focus on tasks and activities.
-
Reduced Impulsivity: Medication can help mitigate impulsive behaviors, enabling individuals to think before acting and make better decisions.
-
Better Behavioral Control: By regulating brain chemistry, medication can assist in managing hyperactivity and disruptive behaviors.
-
Enhanced Academic and Occupational Performance: Improved attention and impulse control can lead to better performance at school or work, ultimately boosting self-esteem and confidence.
Therapy for ADHD
While medication can effectively alleviate symptoms of ADHD, it may not address the underlying issues or provide individuals with the necessary skills to cope with challenges effectively. Therapy, therefore, plays a crucial role in comprehensive ADHD treatment by addressing the emotional, behavioral, and cognitive aspects of the disorder. Common types of treatment for ADHD include:
-
Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy aims to modify specific behaviors associated with ADHD, such as impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity. Techniques such as reinforcement, goal setting, and self-monitoring help individuals develop strategies to manage their symptoms effectively.
-
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to ADHD-related difficulties. CBT empowers individuals to navigate challenges more effectively and build resilience by promoting adaptive thinking and problem-solving skills.
-
Parent Training and Education: Parent training programs provide parents with valuable skills and strategies for managing their child’s ADHD symptoms. These programs focus on effective discipline techniques, communication strategies, and creating structured environments to support the child’s success.
-
Social Skills Training: Many individuals with ADHD struggle with social interactions and forming meaningful relationships. Social skills training helps individuals develop essential social skills such as communication, empathy, and conflict resolution, improving their interpersonal relationships and overall quality of life.
The Benefits of Combining Medication and Therapy
While both medication and therapy can be effective standalone treatments for ADHD, research suggests that combining the two approaches can yield even more significant benefits. The synergistic effects of medication and therapy address the multifaceted nature of ADHD, providing individuals with comprehensive support to manage their symptoms and improve their overall functioning.
-
Comprehensive Symptom Management: Medication helps alleviate core symptoms of ADHD, while therapy equips individuals with skills and strategies to cope with challenges effectively. Together, these approaches provide comprehensive symptom management that addresses the disorder’s neurobiological and behavioral aspects.
-
Skill Building and Coping Strategies: Therapy helps individuals develop essential skills such as organization, time management, and emotional regulation, complementing the symptom relief medication provides. These skills are crucial for long-term success in managing ADHD symptoms and navigating daily life.
-
Improved Treatment Adherence: Therapy can enhance individuals’ understanding of their ADHD and the importance of adhering to medication regimens. Therapy sessions provide opportunities for education, problem-solving, and addressing medication-related concerns, ultimately improving treatment adherence and outcomes.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: By addressing the diverse needs of individuals with ADHD, the combination of medication and therapy can lead to significant improvements in functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life. This holistic approach empowers individuals to thrive despite the challenges associated with ADHD.
Conclusion
ADHD treatment is most effective when approached from a comprehensive perspective that combines medication and therapy. By addressing the disorder’s neurobiological and behavioral aspects, this integrated approach provides individuals with the support, skills, and strategies they need to manage their symptoms successfully and lead fulfilling lives.